To watch a global variable in arm cortex debugging:
1. As the variable is not local anymore we will not see the variable in local windows in the debugging mode
2. we need to click view and then click watch and in the watch window we need to add the variable that we want to watch.
for example for the code below:
int counter = 0;
int main(){
while (counter< 21){
counter++;
}
return 0;
}
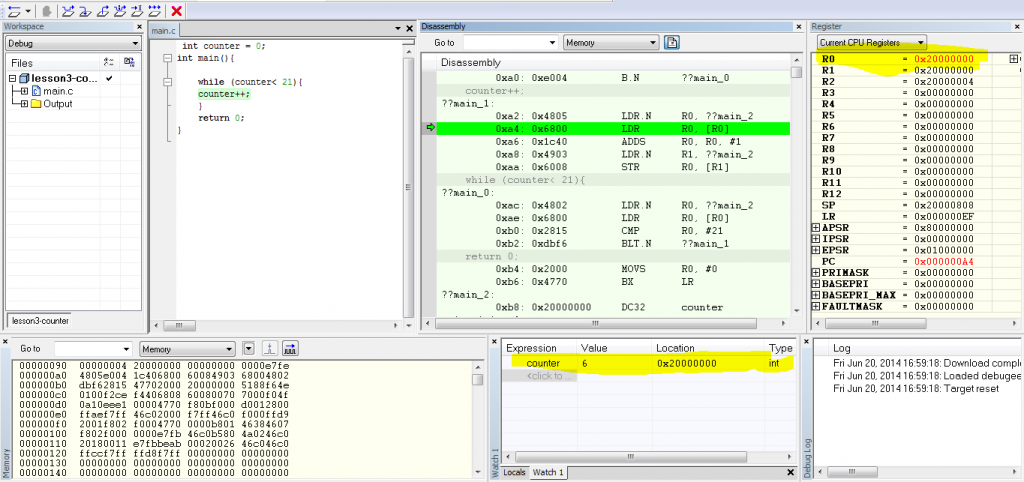
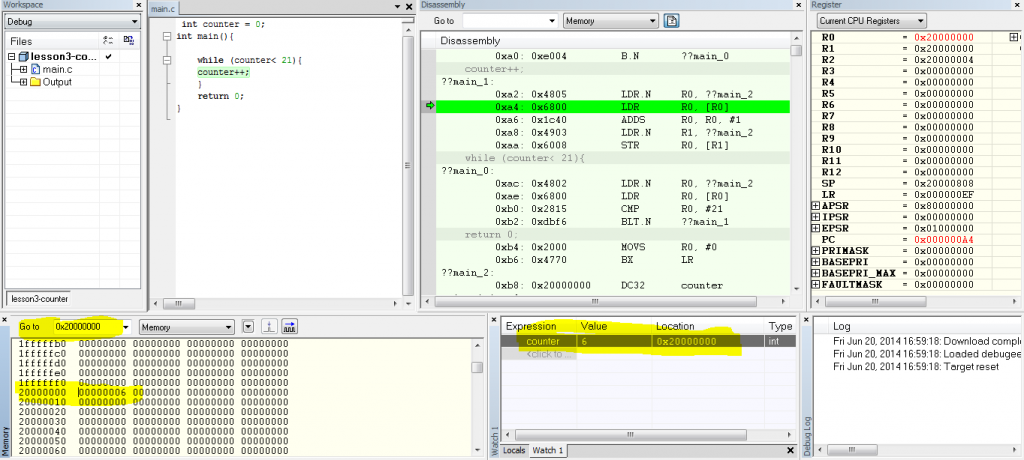
to see counter we need to add watch window. now click the disassemble window to watch the instructions executing:
1. when LDR.N instruction executes: R0 register loads the “address” of the “counter” variable.
2. next LDR instruction loads R0 again but this time the “value” of the “address” R0 was holding loads to R0
3. next add instruction adds 1 to the value of R0
4. next LDR.N instruction loads the “address” of the “counter” variable to R1
5. Next STR instruction store the “value” of “R0″ to the “address” which “R1″ is pointing to
when this instruction executes > the value transfer to the address to counter. The way how arm processor works is an example of RISC = Reduced Instruction Set Computing comparing to CISC = Complex Instruction Set Computing like x86v in personal computer.
in RISC > memory can only read by “Load” instruction and all data manipulation occurs in the registers and then modified data stored back into the memory by special str / store instructions.
Not all the data manipulation needs to happened in the register but can be happened in the memories directly.
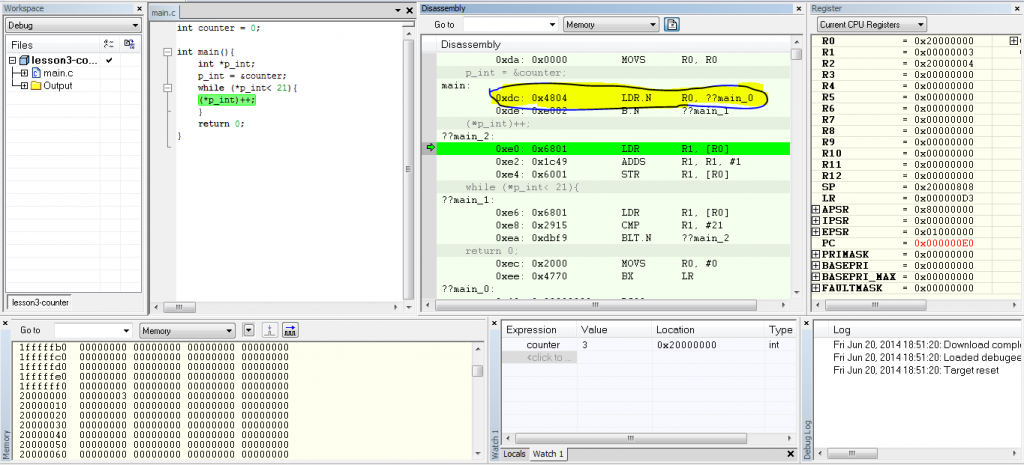
C language can be used to hole this memory address by using a spacial variable called pointers.
so the above program can be written as:
int counter = 0;
int main(){
int *p_int;
p_int = &counter;
while (*p_int< 21){
(*p_int)++;
}
return 0;
}
LDR.N is moved to main function and the 2nd LDR.N from the “without declaring pointer” code is removed from the assembly code, that increase the efficiency of the code and simplified the code.



Recent Comments